- 05 May 2023
CS3MESH4EOSC was mentioned as a H2020 project that is contributiong to the development and implementation of the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC). CS3MESH4EOSC joined the projects Cos4Cloud and TRIPLE under the EU Horizon Results Booster, an initiative that enables the these projects to achieve a higher societal impact. These three projects are mentioned in the "Exemplary Digital Services Enabling
Open Science" report, published in April 2023.
The European Open Science Cloud (EOSC) initiative aims to provide a federated and open multi-disciplinary environment where researchers, innovators, companies and citizens can publish, find and reuse data, tools and services for research, innovation and educational purposes. EOSC is envisioned to foster a change of culture across scientific communities and research infrastructures towards Open Science, developing a ‘Web of FAIR Data and services’ for science in Europe upon which a wide range of value-added services can be built and exploited across countries and scientific disciplines.
By establishing this collaboration, Cos4Cloud, TRIPLE and CS3MESH4EOSC are working together to disseminate their practical results and showcase their potential impact on the uptake of Open Science practices across different communities.
Enabling Open Science through digital services
Ensure that citizen science services continue to be made available on the EOSC to:
- Improve citizen science as an approach for decision-making and SDG monitoring
- Create and strengthen networks of citizen observatories
- Increase integration of citizen science data with existing SDG monitoring and reporting
Truly enforce Open Science and Open Access by:
- Allowing users to discover and visualise search results through a series of innovative services and tools
- Developing software following open standards and making it available under permissive open source licences. The advantage of the open source approach is that the software can easily be migrated to other systems and thus lock-in effects are avoided. This also means that the innovative visual discovery services developed in TRIPLE can be easily connected to other data sources and integrated in other platforms and infrastructures.
- Enabling visual discovery services, such as in GoTriple, that do not only include scholarly articles, but enable a fully integrated visual search with a wide variety of scholarly outputs, including research data and scientific projects. This provides an important contribution to the digitisation of science that makes research outcomes beyond scientific publications increasingly important.
Unleashing collaborative research potential with Science Mesh’s seamless data platform
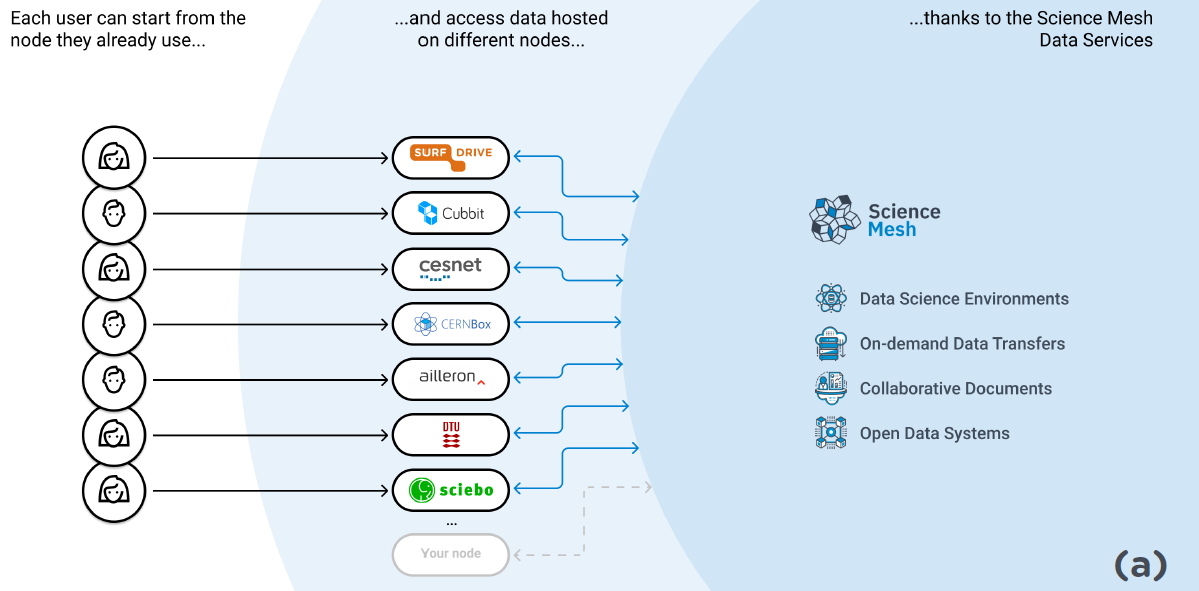
CS3MESH4EOSC’s main asset - the Science Mesh - addresses the challenges of fragmentation in file and application services, digital sovereignty, and the application of FAIR principles in the everyday practice of researchers. Using vendor-neutral Application Programming Interfaces and protocols, the Science Mesh will create an interoperable federation of data and higher level services to enable friction-free collaboration between European researchers. Ultimately, the Science Mesh will engage with researchers by integrating with their local sync-and-share service providers, enabling them to easily implement and embrace Open Science practices. The Science Mesh key technology consists of an interoperability platform (or ‘federated layer’) which enables different EFSS services to communicate with one another. Through this federated layer, the Science Mesh focuses on enabling four specialised data service categories:
- Open Data Systems: end-users will be able to organise data via tagging and metadata assignment, creating a published and referable dataset that will ultimately be deposited to an open data repository, archive, or library for curation and long-term archiving. The Science Mesh will make use of persistent identifiers (e.g., DOIs and ORCID iDs) to facilitate this.
- Collaborative Documents: end-users will be able to use collaborative editing applications via the Science Mesh to simultaneously edit various types of documents.
- Data Science Environments: end-users will be able to access remote execution environments to replay (and modify) analysis algorithms without a need to set up upfront accounts in the remote system. This would be accessible via the web interface at the remote sites of researchers, allowing them to work on algorithms and data processing programs interactively.
- On-demand data transfers: this data service is dedicated to the integration of large data transfers in the Science Mesh, allowing efficient data-based collaboration on on-demand basis - opposite to ‘a priori’ planned data processing workflows.